学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sK411B71e
JDBC 技术概述
jdbc 技术概念和理解
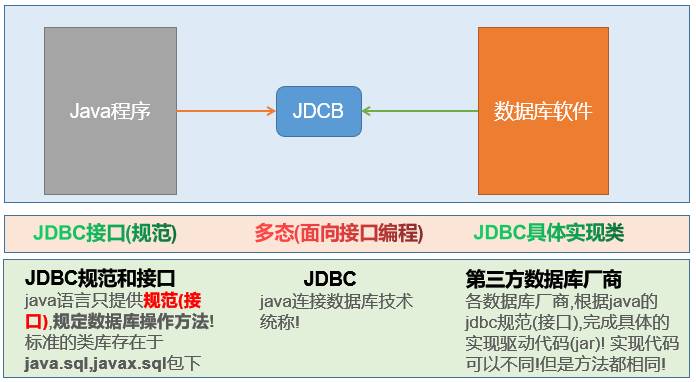
JDBC 概念:Java Database Connectivity | Java 连接数据库技术!
通俗点说,在Java代码中,使用JDBC提供的方法,可以发送字符串类型的SQL语句到数据库管理(MySQL,Oracle等),并且获取语句执行结果!进而实现数据库数据CURD操作的技术!
JDBC 本质理解
总结
jdbc 是(Java Database Connectivity)单词的缩写,翻译为 java 连接数据库
jdbc 是 java 连接数据库的技术统称
jdbc 是 java 语言的规范(接口)和各个数据库厂商的实现驱动(jar)组成
jdbc 是一种典型的面向接口编程
jdbc 优势
a. 只需要学习 jdbc 规范接口的方法,即可操作所有的数据库软件
b. 项目中期切换数据库软件,只需要更换对应的数据库驱动jar 包,不需要更改代码
jdbc核心api和使用路线
jdbc 技术组成
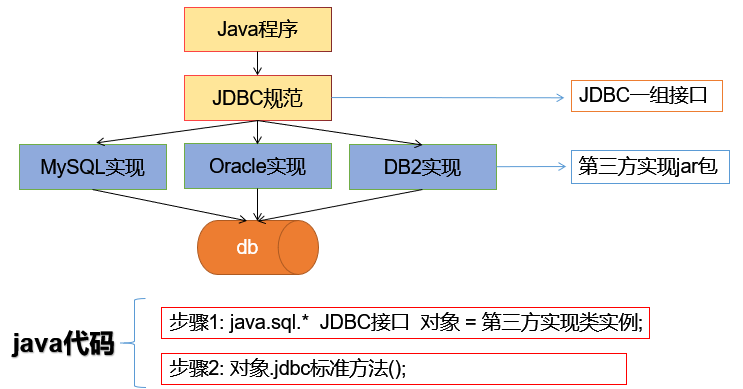
jdk 下 jdbc 规范接口,存储在 java.sql 和 javax,sql 包中的 api
为了项目代码的可移植性,可维护性,SUN 公司从最初就制定了 Java 程连接各种数据库的统一接口规范,这样的话,不管是连接哪一种 DBMS 软件,Java 代码可以保持一致性。
各个数据库厂商提供的驱动 jar 包
因为各个数据库厂商的 DBMS 软件各有不同,那么内部D何通过 sql 实现增、删、改、查等管理数据,只有这个数据库厂商自己更清楚,因此把接口规范的实现交给各个数据库厂商自己实现。
jar 包是什么?
java 程序打成的一种压包格式,你可以将这些 jar 包引入你的项目中,然后你可以使用这个java 程序中类和方法以及性了!
涉及具体核心类和接口
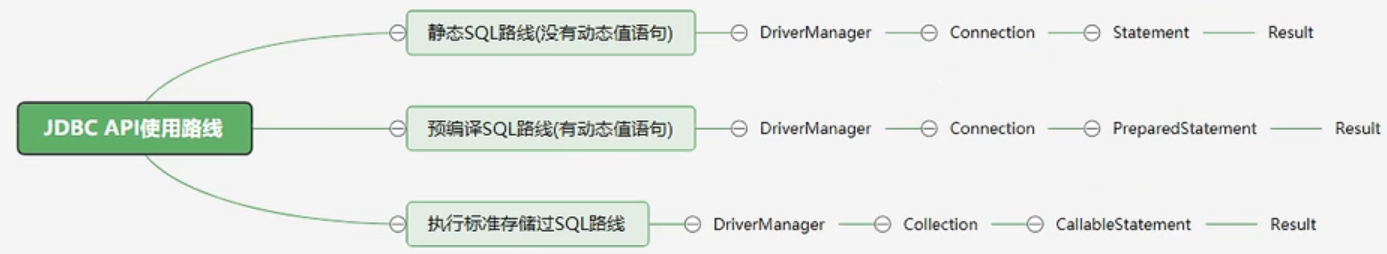
jdbc api使用路线
JDBC核心API
引入 mysql-jdbc 驱动jar
最新教程请访问:MySQL下载、安装及Java JDBC配置连接数据库
驱动 jar 版本选择
我这里选择mysql 8.0.27 + 8.0.27的jar驱动
java 工程导入依赖
a. 项目创建lib文件夹
b. 导入驱动依赖 jar 包
c. jar 包右键-添加为项目依赖
jdbc 基本使用步骤分析
- 注册驱动
- 获取连接
- 创建发送 sql 语句对象
- 发送 sql 语句,并获取返回结果
- 结果集解析
- 资源关闭
基于 statement 演示查询
下面演示了java查询db01数据库中的emp表中的id, name, age, entrydate等字段的数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| package com.atxiong.api.statement;
import com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver;
import java.sql.*;
public class StatementQueryPart {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
Connection connection = DriverManager.
getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db01", "root", "mysql");
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select id, name, age, entrydate from emp;";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");
Date entrydate = resultSet.getDate("entrydate");
System.out.println(id+"--"+name+"--"+age+"--"+entrydate);
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
基于 statement 方式问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
| package com.atxiong.api.statement;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StatementUserLoginPart {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter username: ");
String account = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter password: ");
String password = scanner.nextLine();
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection1 = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01", "root", "mysql");
Statement statement = connection1.createStatement();
String sql = "select id, name, age, entrydate from emp where account = '" + account + "' and password = '" + password + "';";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection1.close();
}
}
|
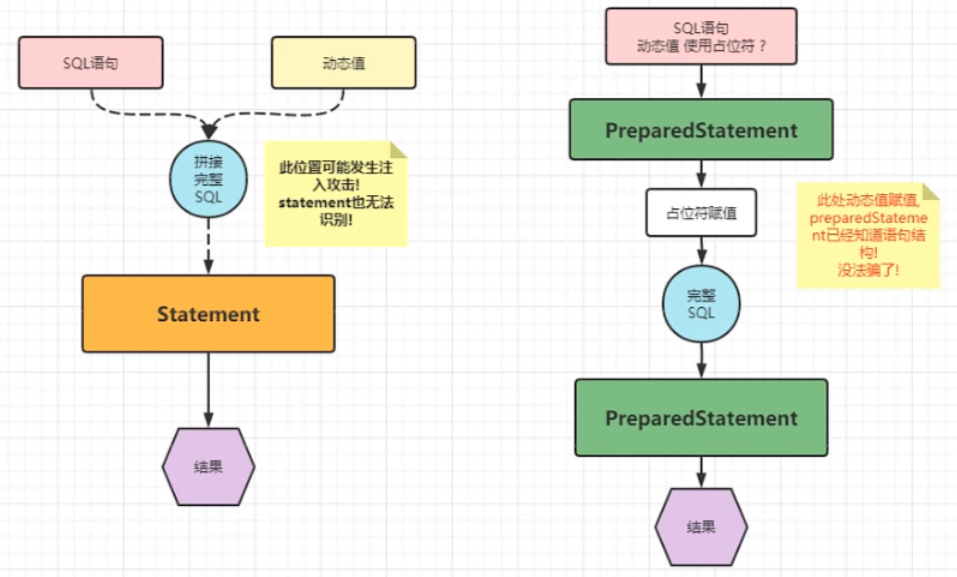
存在问题:
SQL 语句需要字符申拼接比较麻烦
只能拼接字符里类型,其他的数据库类型无法处理
可能发生注入攻击
动态值充当了 SQL 语句结构,影响了原有的查询结果!
解决方法:使用preparedStatement
基于 preparedStatement 方式优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| package com.atxiong.api.preparedstatement;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PreparedStatementUserLoginPart {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter username: ");
String account = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter password: ");
String password = scanner.nextLine();
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?user=root&password=mysql");
String sql = "select * from emp where account = ? and password = ?;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,account);
preparedStatement.setObject(2,password);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
基于 preparedStatement 演示 curd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
| package com.atxiong.api.preparedstatement;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.*;
public class PreparedStatementCrudPart {
@Test
public void testInsert() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01", "root", "mysql");
String sql = "insert into user (name,age,status,gender) values (?,?,?,?);";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "XiaoMing");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 23);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, 0);
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "男");
int resultSet = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (resultSet > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("插入失败!");
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?user=root&password=mysql");
String sql = "update user set name = ?, age = ? where name = ?;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "xiaozhao");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 38);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "xiaoming");
int result = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (result > 0) {
System.out.println("修改成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("修改失败!");
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?user=root&password=mysql");
String sql = "delete from user where name = ?;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "xiaozhao");
int result = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (result > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败!");
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelect() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?user=root&password=mysql");
String sql = "select name, age, status, gender from user;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<Map<Object, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
while (resultSet.next()){
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
Object object = resultSet.getObject(i);
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
map.put(columnLabel, resultSet.getObject(columnLabel));
}
list.add(map);
}
for (Map map : list) {
System.out.println(map);
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
preparedStatement 使用方式总结
使用步骤总结
- 注册驱动
- 获取连接
- 编写
SQL语句 - 创建
preparedStatement并传入SQL语句结构 - 占位符赋值
- 发送SQL语句,并获取结果
- 结果集解析
- 关闭资源
使用API总结
注册驱动
方案1:调用静态方法,但是会注册两次
1
| DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver());
|
方案2:反射触发
1
| Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
|
获取连接
1
2
3
4
5
| Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection();
|
创建statement
静态
1
| Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
|
预编译(推荐)
1
| PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.preparedStatement(sql语句结构):
|
占位符赋值
1
| preparedStatement.setObject(?的位置 从左到右 从1开始, 值)
|
发送 SQL 语句获取结果
1
2
| int rows = executeUpdate();
Resultset resultSet = executeQuery();
|
查询结果集解析
移动光标指向行数据 next() if(next()) while(next())
获取列的数据即可 get类型(int 列的下角标 从1开始 | int 列的label (别名或者列名)
获取列的信息 getMetadata(); ResultsetMetaData对象 包含的就是列的信息
getColumnCount(); | getcloumnLebal(index)
关闭资源
1
2
3
| resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close()
connection.close();
|
JDBC扩展提升
自增长主键回显实现
功能需求
java 程序获取插入数据时 mysql 维护自增长维护的主键 id 值这就是主键回显
作用:在多表关联插入数据时,一般主表的主键都是自动生成的,所以在插入数据之前无法知道这条数据的主键但是从表需要在插入数据之前就绑定主表的主键这是可以使用主键回显技术.
功能实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| package com.atxiong.api.preparedstatement;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.*;
public class PreparedStatementOtherPart {
@Test
public void returnPrimaryKey() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?user=root&password=mysql");
String sql = "insert into user (name,age,status,gender) values (?,?,?,?);";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "XiaoMing");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 23);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, 0);
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "男");
int result = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (result > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功!");
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
resultSet.next();
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
System.out.println("id= " + id);
}else {
System.out.println("插入失败!");
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
批量数据插入性能提升
功能需求:实现高效的批量插入数据
功能实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
@Test
public void testBatchInsert() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01?rewriteBatchedStatements=true", "root", "mysql");
String sql = "insert into user (name,age,status,gender) values (?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "Xi" + i);
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 23);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, 0);
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "男");
preparedStatement.addBatch();
}
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间:" + (end - start));
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
jdbc 中数据库事务实现
章节目标
- 使用 jdbc 代码,添加数据库事务动作!
- 开启事务
- 事务提交 / 事务回滚
数据库表数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # 继续在atguigu的库中创建银行表
CREATE TABLE Bank(
Id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '账号主键',
account VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL UNIQUE COMMENT '账号',
money INT UNSIGNED COMMENT '金额,不能为负值');
INSERT INTO Bank(account, money) VALUES ('xiong', 1000), ('shen', 1000);
|
代码结构设计
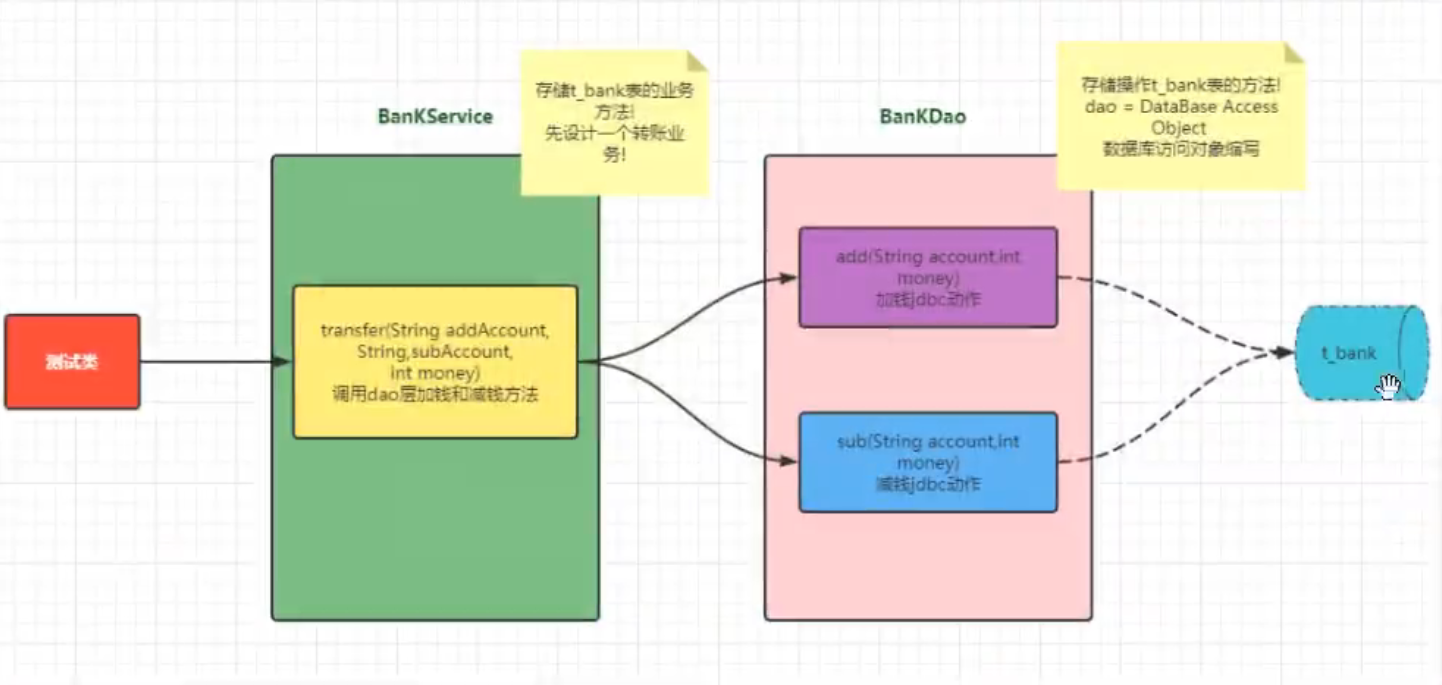
jdbc事务实现
例子实现:
银行卡业务方法以及测试方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| package com.atxiong.api.transaction;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BankService {
@Test
public void transferTest() throws Exception {
BankService bankService = new BankService();
bankService.transfer("xiong", "shen", 500);
}
public void transfer(String addAccount, String subAccount, int money) throws Exception{
BankDao bankDao = new BankDao();
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db01", "root", "mysql");
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
bankDao.add(addAccount, money, connection);
System.out.println("---------");
bankDao.sub(subAccount, money, connection);
connection.commit();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
connection.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
connection.close();
}
}
}
|
Bank表的数据库操作方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| package com.atxiong.api.transaction;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BankDao {
public int add(String account, int money, Connection connection) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
String sql = "update bank set money = money + ? where account = ?;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, money);
preparedStatement.setObject(2, account);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
System.out.println("加钱成功!");
return rows;
}
public int sub(String account, int money, Connection connection) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
String sql = "update bank set money = money - ? where account = ?;";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, money);
preparedStatement.setObject(2, account);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
System.out.println("减钱成功!");
return rows;
}
}
|
Druid连接池技术
连接性能消耗问题分析
由于连接创建和回收的会消耗大量时间,甚至可能大于连接使用的时间,因此可以想办法复用connection,于是出现了连接池。
数据库连接池的作用
总结缺点:
不使用数据库连接池,每次都通过DriverManager获取新连接,用完直接抛弃断开,连接的利用率太低,太浪费。
对于数据库服务器来说,压力太大了。我们数据库服务器和 Java 程序对连接数也无法控制,很容易导致数据库服务器崩溃。
我们就希望能管理连接。
- 我们可以建立一个连接池,这个池中可以容纳一定数量的连接对象,一开始,我们可以先替用户先创建好一些连接对象,等用户要拿连接对象时,就直接从池中拿,不用新建了,这样也可以节省时间。然后用户用完后,放回去,别人可以接着用。
- 可以提高连接的使用率。当池中的现有的连接都用完了,那么连接池可以向服务器申请新的连接放到池中。
- 直到池中的连接达到“最大连接数“,就不能在申请新的连接了,如果没有拿到连接的用户只能等待。
市面常见连接产品和对比
JDBC的数据库连接池使用 javax.sql.DataSource接口进行规范,所有的第三方连接池都实现此接口,自行添加具体实现!也就是说,所有连接池获取连接的和回收连接方法都一样,不同的只有性能和扩展功能!
DBCP 是 Apache 提供的数据库连接池,速度相对 c3p0 较快,但因自身存在BUG
C3P0 是一个开源组织提供的一个数据库连接池,速度相对较慢,稳定性还可以
Proxool 是 sourceforge 下的一个开源项目数据库连接池,有监控连接池状态的功能稳定性较 c3p0 差一点
Druid 是阿里提供的数据库连接池,据说是集DBCP 、C3P0 、ProxooL 优点于一身的数据库连接池,要要国货之光!!!!
国货之光druid连接池使用
使用前要导入druid工具类的 jar
硬编码方式(了解,不推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
@Test
public void druidHard() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("mysql");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///db01");
Connection connection = dataSource .getConnection0);
connection.close();
}
|
软编码方式
外部配置文件
存放在src/druid.properties
1
2
3
4
5
|
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username=root
password=mysql
url=jdbc:mysql:///db01
|
druid声明代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Test
public void druidSoft() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream ips = DruidDemo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid");
properties.load(ips);
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
}
|
JDBC使用优化以及封装
jdbc工具类封装 v1.0
用于封装注册驱动(连接池)、获取连接、回收连接等连接相关的代码
外部配置文件
位置: src/druid.properties
1
2
3
4
5
|
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username=root
password=mysql
url=jdbc:mysql:///db01
|
工具类代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| package com.atxiong.api.utils;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
public static void freeConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
connection.close();
}
}
|
jdbc工具类封装 v2.0
优化工具类v1.0版本,考虑事务的情况下!如何使一个线程的不同方法获取同一个连接?
ThreadLocal的介绍:
JDK1.2的版本中就提供java.lang.ThreadLocal,为解决多线程程序的并发问题提供了一种新的思路使用这个工具类可以很简洁地编写出优美的多线程程序。通常用来在在多线程中管理共享数据库连接、Session等
ThreadLocal用于保存某个线程共享变量,原因是在 Java 中,每一个线程对象中都有一个ThreadLocalMap<ThreadLocal,Object>,其 key 就是一个ThreadLocal,而object即为该线程的共享变量。而这个 map 是通过ThreadLocal的 set 和 get 方法操作的。对于同一个static ThreadLocal,不同线程只能从中 get,set,remove 自己的变里,而不会影响其他线程的变里。
- ThreadLocal对象.get: 获取 ThreadLocal 中当前线程共享变量的值。
- ThreadLocal对象.set: 设置 ThreadLocal 中当前线程共享变里的值。
- ThreadLocal对象.remove: 移除 ThreadLocal 中当前线程共享变量的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| package com.atxiong.api.utils;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtilsV2 {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = JdbcUtilsV2.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = tl.get();
if (connection == null) {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
public static void freeConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = tl.get();
if (connection != null) {
tl.remove();
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
connection.close();
}
}
}
|
高级应用层封装 BaseDao
用于封装查询方法以及非查询方法的代码
基本上每一个数据表都应该有一个对应的 DAO 接口及其实现类,发现对所有表的操作(增、删、改、查)代码重复度很高,所以可以抽取公共代码,给这些DAO 的实现类可以抽取一个公共的父类,我们称为 BaseDao。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
| package com.atxiong.api.utils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class BaseDao {
public int executeUpdate(String sql, Object ... params) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtilsV2.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i, params[i - 1]);
}
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
if (connection.getAutoCommit()) {
JdbcUtilsV2.freeConnection();
}
return rows;
}
public <T> List<T> executeQuery(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object ... params) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtilsV2.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
if (params != null && params.length != 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i, params[i - 1]);
}
}
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
while (resultSet.next()){
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
String propertyName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, value);
}
list.add(t);
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
if (connection.getAutoCommit())
JdbcUtilsV2.freeConnection();
return list;
}
}
|






